Tracking gas fees on Ethereum and other blockchains is essential for anyone transacting in the crypto world. Whether you’re swapping tokens, minting NFTs, or deploying smart contracts, knowing how to track gas fees in real time can save you from costly surprises. With tools like Etherscan Gas Tracker and Blocknative Gas Estimator, users can monitor live Ethereum gas prices, estimate transaction costs, and avoid peak congestion periods.
When your wallet runs dry, finding the fastest way to get ETH for gas can help you avoid delays and transaction failures.
Investors and developers alike are also exploring how to calculate gas fees and use platforms that offer gas fee live charts for strategic planning. With Ethereum upgrades on the horizon, understanding the best tools to track real-time gas fees and learning the fastest way to get ETH for gas is more critical than ever.
Gas fees can fluctuate rapidly, affecting the cost of sending tokens, swapping assets, or interacting with decentralized applications (dApps). Understanding how to track these fees can help you save money and make informed decisions.
In this guide, we’ll explore what gas fees are, why they matter, and how you can monitor them effectively.
What Are Gas Fees?
Gas fees are the costs required to perform transactions on a blockchain network, like Ethereum. They’re measured in units called “gwei,” which are fractions of the ETH. These fees compensate network validators for processing and confirming your transactions.
Key Points:
- Gas fees vary based on network demand.
- Higher demand can lead to higher fees.
- Fees are paid in the network’s native cryptocurrency (e.g., ETH)
Why Do Gas Fees Fluctuate?

Gas fees aren’t fixed; they change depending on several factors:
- Network Congestion: When many users are transacting simultaneously, fees increase.
- Transaction Complexity: More complex operations (like smart contract interactions) require more gas.
- Time of Day: Fees can be lower during off-peak hours.
Real-World Example:
Imagine you’re trying to buy an NFT during peak time or during the launch of a NFT when many traders are trying to transact on the blockchain to make the transaction successful. Keep in mind you are not alone, everyone else is doing the same, leading to network congestion and higher gas fees. By tracking gas fees, you could choose a less busy time to make your purchase, saving on costs. There are still ways to reduce eth gas fee you just have to aware about it.
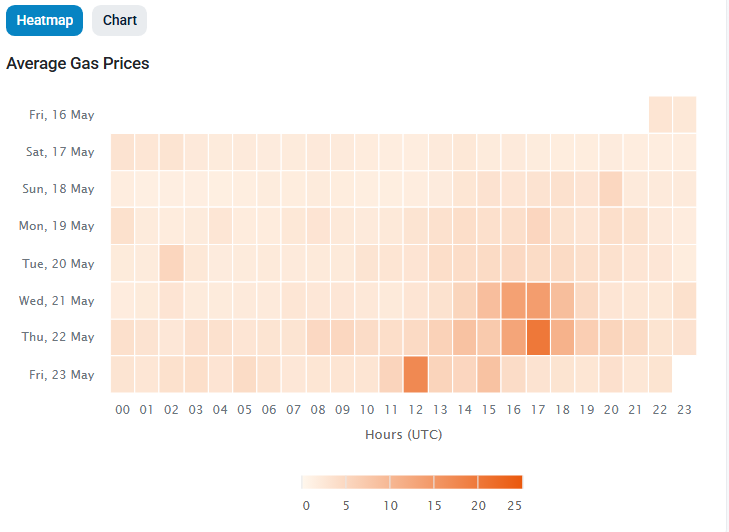
Tools to Track Gas Fees – Monitoring Real Time Gas Fees on Ethereum

Several tools can help you monitor gas fees in real-time:
- Etherscan Gas Tracker: Provides current gas prices and historical data.
- Blocknative Gas Estimator: Offers live gas price estimates and notifications.
- QuickNode Gas Tracker: Displays real-time gas prices and transaction cost estimations.
- Milk Road Ethereum Gas Fees: Shows gas fee trends and optimal transaction times.
Real-World Example:
Suppose you’re planning to swap tokens on a decentralized exchange. By checking the Etherscan Gas Tracker, you notice that gas fees are currently high. You decide to wait until fees drop, saving money on your transaction to avoid high gas fee.
Strategies to Minimize Gas Fees
Being proactive can help you reduce gas fees:
- Transact During Off-Peak Hours: Early mornings or weekends often have lower fees.
- Use Layer 2 Solutions: Platforms like Arbitrum or Optimism offer lower fees.
- Set Gas Limits: Manually adjust gas settings in your wallet to control costs. Manual adjusting can help you get the transaction done only when gwei meets your budget but if network congestion is very high. then you have to wait to cool down the network or increase your budget to make the transaction successful.
- Batch Transactions: You’re sending funds to multiple addresses. Instead of sending separate transactions, you batch them into one, reducing the total gas fees incurred.
Understanding Gas Fee Calculations

Gas fees are calculated using the formula:
Gas Units (limit) x (Base Fee + Tip)
- Gas Units: The amount of computational work required.
- Base Fee: Set by the network, fluctuates with demand.
- Tip (Priority Fee): An optional amount to incentivize for faster transaction processing.
Real-World Example:
Let’s suppose you’re sending ETH with a gas limit of 21,000 units. The base fee is 50 gwei, and you add a tip of 10 gwei. Your total gas fee would be:
21,000 x (50 + 10) = 1,260,000 gwei
Which equals 0.00126 ETH.
Impact of Ethereum Upgrades on Gas Fees
Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (The Merge) aimed to improve scalability and reduce energy consumption. However, it didn’t directly lower gas fees.
After The Merge, you notice that while transaction speeds have improved, gas fees remain high during peak times. By utilizing Layer 2 solutions, you achieve lower fees and faster confirmations.
You Can Use Polygon for Lower Fees and Faster Confirmations
To avoid high gas fees on Ethereum, you can use Polygon for budgeted and faster transaction but you will miss the real catch.
- Polygon (MATIC): Offers minimal fees and fast transactions.
- Arbitrum – Fast, low-cost Ethereum Layer 2 solution.
- Optimism – Scalable Ethereum Layer 2 with growing dApp support.
Let’s say you’re deploying a smart contract and want to minimize costs. By choosing Polygon over Ethereum, you significantly reduce gas fees while maintaining functionality. But keep in mind after using polygon network for your smart contract, all future transactions will be going through polygon network which is cheap and fast but you will lose the edge of using ethereum native blockchain having liquidity in billions of dollars. So it is actually a trade off using cheap network with less liquidity & vice versa.
Final Thoughts on How to Track Gas Fees
In today’s fast-moving crypto environment, learning how to track gas fee is more than just a useful skill—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re sending ETH, trading tokens, or interacting with smart contracts, understanding gas fees helps you avoid overpaying and keeps your transactions smooth.
By using real-time gas fee tracking tools, Ethereum gas fee live charts, and platforms that monitor cross-chain gas fees, users can make smarter, faster, and more cost-effective decisions. From calculating gas fees on Ethereum to tracking them across multiple blockchains, the tools and strategies will help you to stay ahead of network congestion and optimize your crypto activity accordingly.
FAQ
Q: What is a gas fee?
A gas fee is the cost required to perform a transaction on a blockchain network, compensating validators for processing your request.
Q: Why do gas fees fluctuate?
Fees change based on network demand, transaction complexity, and time of day.
Q: How can I check current gas fees?
Use tools like Etherscan Gas Tracker for real-time data.
Q: Are there ways to reduce gas fees?
Yes, by transacting during off-peak hours, using Layer 2 solutions, and batching transactions.
Q: Do other blockchains have gas fees?
Yes, most blockchains have transaction fees, though the amounts and structures vary.














