The IMF isn’t against Bitcoin on paper. But in practice, it ties financial support to policies that discourage crypto adoption. Countries seeking IMF loans often must align with guidelines that classify cryptocurrencies as financial risks.
Bitcoin Setbacks in El Salvador, Argentina, and Central African Republic
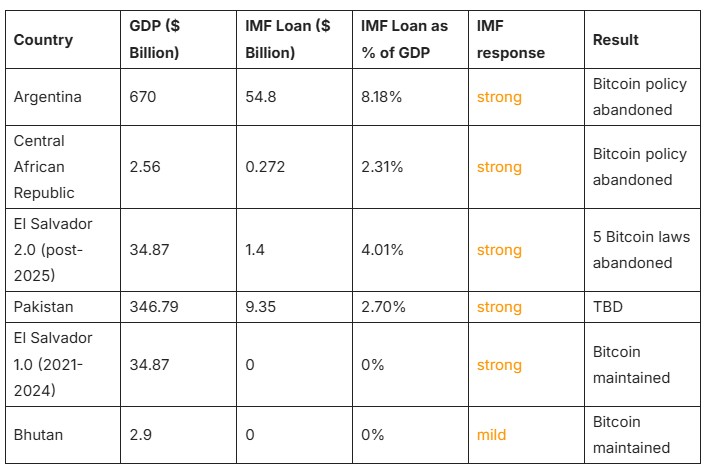
El Salvador made headlines in 2021 for making Bitcoin legal tender. But its continued negotiations with the IMF later resulted in scaled-back implementation. Similar stories played out in Argentina and the Central African Republic.
These three cases show how Bitcoin-friendly policies quickly become diluted once the IMF becomes involved.
Why Pakistan’s Bitcoin Plans Trigger IMF “Serious Concerns”
Pakistan is one of the latest nations facing IMF scrutiny over digital asset plans. Despite growing interest, the country’s central bank has signaled hesitation, largely due to IMF warnings.
In early 2025, Pakistani officials hinted at exploring crypto solutions to combat inflation and boost financial inclusion. But during ongoing IMF loan discussions, the organization flagged these proposals as high-risk.
The IMF’s formal statements mentioned “serious concerns” over financial crime, volatility, and systemic risk. While these issues are not unique to crypto, their mention in loan talks has a chilling effect.
The IMF’s influence on Pakistan mirrors the trend seen in other debt-dependent economies: bold crypto initiatives get sidelined or postponed indefinitely.
Strategy’s $6B Bitcoin in Unrealized Losses
While nation-states face IMF pressure, corporations like Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) encounter their own risks. The company is now the target of five nearly identical lawsuits.
Strategy’s high-profile Bitcoin purchases totaled $7.7 billion, much of it near local price peaks. As of Q2 2025, the company is sitting on $6 billion in unrealized losses. Now, multiple law firms have filed class-action suits, accusing Strategy of misleading investors.
The legal basis centers on the claim that Strategy downplayed risk and overstated profitability projections in public statements. According to legal experts, these copycat filings are common in securities fraud cases, where law firms compete to become lead counsel for higher earnings.
This case highlights the tightrope that institutions walk when adopting Bitcoin: the promise of upside meets the reality of legal and financial scrutiny when prices fall.
China’s Stablecoin Edge: WeChat Pay, Alipay, and the Digital Yuan
While the IMF discourages crypto adoption, China is quietly building a digital payments powerhouse through existing platforms like WeChat Pay and Alipay.
Top economists in China argue that these services function like stablecoins. They are digital, fast, and pegged 1:1 to the yuan, backed by central bank reserves. Unlike Western stablecoins, China’s version is deeply integrated with its real economy and regulatory framework.
Recent research shows that China could outpace the West by promoting digital yuan use through these platforms. Rather than issuing new tokens, the state leverages existing infrastructure to expand globally.
This model presents a stark contrast to IMF-loan nations that retreat from crypto. China embraces digital money without risking IMF disapproval because it retains full control and transparency.
Bolivia’s 630% Crypto Surge: A New Model for National Adoption?
Bolivia’s crypto activity exploded by 630% after it lifted a formal ban. What happened next could serve as a blueprint for crypto adoption under tight regulatory oversight.
The Central Bank of Bolivia reported $430 million in digital asset transactions over 12 months, mostly from individual users. Regulatory updates have allowed banks to interact with exchanges, while the state-run energy firm now uses crypto for fuel imports.
Legal reforms like Decree 5384 and Resolution 082/2024 established new licensing systems for virtual asset service providers. Workshops across the country have been launched to educate users about wallet safety, scams, and price volatility.
Instead of blanket bans or unchecked adoption, Bolivia is carving a middle path—one that embraces digital assets under a clear legal and compliance framework.
Conclusion:
The Fight for Bitcoin’s Future Isn’t Over: The IMF’s behind-the-scenes role in deterring national Bitcoin adoption is clear. But it’s also becoming increasingly obvious that digital assets are not going away. Countries like Bolivia are adapting, China is innovating, and corporate players like Strategy are weathering the risks.
Whether or not Bitcoin becomes a national currency in more places, the momentum is shifting. Grassroots adoption, legal clarity, and digital payment innovations are moving forward—sometimes around, sometimes through the roadblocks put up by institutions like the IMF.
Latest Crypto News;
- Bitcoin Hits $40B in Derivative Market as Corporations Rush Into Crypto Market
- Why US Crypto Stocks Surged?
- Crypto News: Bitcoin Rebounds, Coinbase MiCA license, OKX IPO
- 7 Real-Time Shifts Driving Fear and Opportunity in the Crypto Market
- Solana, XRP, and Dogecoin ETFs
- Project 11 Raised $6M to Fix Flaw Behind Bitcoin’s Iron Wall
- Bitcoin Mining Moves to the U.S. as Trade War and Security Fears Grow
- Crypto News Flash: Metaplanet Surpasses Coinbase,
- Is it a Crash or DIP? Bitcoin Rebound, Dogecoin Nosedive and Solana ETF
- Bitcoin Slumps, Ethereum’s $1B Play, and the SEC’s New Stance
- How Wall Street, Germany, and GameStop Are Changing the Rules?
- Ethereum’s $110B DeFi Surge, Bullish and Gemini IPOs
- Paraguay Hack, Circle IPO Boom, and Hong Kong’s Chainlink CBDC Pilot
- Why Michael Saylor Is Betting Big on Bitcoin
- Billionaire’s Conflict Shake-Up and Wake-Up the Crypto Market